The Safety of TMP-SMX Use in Patients Taking an ACE-I or ARB
ABSTRACT
Background: Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) are commonly used medications for hypertension, heart failure, and diabetes. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) is a commonly used antibiotic for many bacterial infections. While hyperkalemia is a known risk of each drug, little has been studied about concomitant use of ACE-I/ARBs and TMP-SMX.
Methods: An exhaustive search of MEDLINE-Ovid, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and International Pharmaceutical Abstracts-Ovid using the search terms TMP-SMX and ACE inhibitor and ARB was done. Eligibility criteria included studies in the English language, studies that included concurrent use of TMP-SMX and ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and studies focused on on-label uses of TMP-SMX. Found studies were evaluated using GRADE criteria.
Results: Three studies met eligibility requirements. One retrospective cohort study showed that in patients with renal insufficiency receiving low dose of TMP-SMX, ACE-I/ARB use was a significant risk factor for developing hyperkalemia (adjusted OR 3.95, 95% CI 1.17-13.4). A large nested case-control study found patients taking an ACE-I/ARB prescribed TMP-SMX had an increased risk of hospitalization with diagnosis of hyperkalemia of when compared with those prescribed amoxicillin (adjusted OR 6.7, 95% CI 4.5-10.0). Another large nested case-control drawn from a similar population found patients taking an ACE-I/ARB had an increased risk of sudden death when prescribed TMP-SMX when compared with those prescribed amoxicillin (adjusted OR 1.54, 95% CI 1.29-1.84).
Conclusion: Studies suggest an increased risk with concurrent ACE-I/ARB and TMP-SMX use. As both are commonly prescribed medications, understanding these risks of concomitant use is important. Risks, including hospitalization and sudden death, are likely related to hyperkalemia and likely increase in patients with existing renal insufficiency. Before prescribing TMP-SMX in patients already taking an ACE-I/ARB, clinicians should consider alternatives. More research is needed to fully understand the risks associated with combining these medications.
Keywords: TMP-SMX, ACE inhibitor, Bactrim, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors, ARB
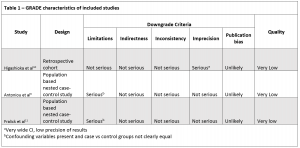
(Click on image to enlarge.)
REVIEWED STUDIES:
Antoniou T, Gomes T, Jurrlink DN, Loutfy MR, Glazier RH, Mamdani MM. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-induced hyperkalemia in patients receiving inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:1045-1049.
Higashioka K, Niiro H, Yoshida K, et al. Renal Insufficiency in Concert with Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone Inhibition Is a Major Risk Factor for Hyperkalemia Associated with Low-dose Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in Adults. Internal Medicine. 2016;55:467-471.
Fralick M, Macdonald EM, Gomes T, et al. Co-trimoxazole and sudden death in patients receiving inhibitors of renin-angiotensin system: population based study. BMJ. 2014;349:g6196.
AUTHOR: Aaron Inouye is currently completing his second year in the School of PA Studies at Pacific University, Oregon. He will graduate with an MS degree in August, 2016.