The Use of Kinect to Improve Balance and Postural Control in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
ABSTRACT
Background: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a leading cause of disability in young adults, affecting women more than men. Many MS patients experience gait difficulties due to muscle weakness and loss of balance and postural control. Standard interventions for maintaining or improving balance are addressed with conventional physical therapy, but this is often costly, time-consuming, and geographically inaccessible, all of which impact patient compliance. The primary goal of this systematic literature review investigates and addresses whether virtual reality therapy using Xbox Kinect improves balance and postural control in MS patients.
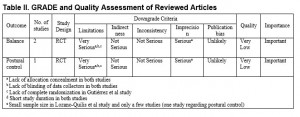
Methods: An exhaustive literature search using MEDLINE-Ovid, Web of Science and CINAHL was performed using keywords: multiple sclerosis, Xbox, and Kinect. All articles were screened with eligibility criteria. The remaining relevant articles were assessed for quality using GRADE.
Results: Two studies met eligibility criteria and were included in this systematic review. Each study was a randomized controlled trial. Both studies demonstrated significant improvement in balance when using the Kinect therapy. Significant improvement in postural control with use of Kinect therapy was also demonstrated in one of the studies.
Conclusion: Virtual reality (VR) Kinect therapy is effective in improving balance and postural control in patients with MS. Although it should not replace conventional therapy as the studies both demonstrated, it can aid as an important alternative to MS patients with mobility and accessibility difficulties and for those who cannot afford costly therapy sessions. Future studies that provide more evidence about patient compliance and cost-effectiveness will help determine the long term effect VR Kinect therapy has on the disease course.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis, Xbox, Kinect
(Click on image to enlarge.)
REVIEWED STUDIES:
Ortiz-Gutiérrez R, Galán-del-Río F, Cano-de-la-Cuerda R, et al. A telerehabilitation program by virtual reality-video games improves balance and postural control in multiple sclerosis patients. NeuroRehabilitation 2013;33:545-554.
Lozano-Quilis J-A, Gil-Gómez H, Gil-Gómez J-A, et al. Virtual Rehabilitation for Multiple Sclerosis Using a Kinect-Based System: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Serious Games 2014;2(2):e12.
AUTHOR: Theresa Jones is currently completing her second year in the School of PA Studies at Pacific University, Oregon. She will graduate with an MS degree in August, 2016.