Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors Can Alleviate Exercise-Induced Skeletal Muscle Ischemia in Males with Muscular Dystrophy
ABSTRACT
Background: Muscular Dystrophy (MD) is a progressive X-linked muscular wasting disease. Glucocorticoids are currently being used to prolong ambulation for 2 to 3 years, but have failed to alleviate muscle ischemia and prevent muscle injury. The muscle ischemia occurs in these patients as a result of mutations in the gene coding for the protein dystrophin important in the protective mechanism otherwise known as functional sympatholysis. Studies on mice deficient in dystrophin found restoration of this mechanism with the use of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. The purpose of this review was to investigate whether PDE5 inhibitors could alleviate exercise-induced skeletal muscle ischemia in human patients with MD.
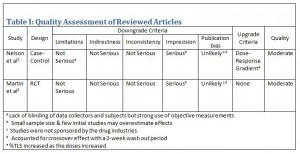
Methods: An exhaustive search of MEDLINE-Ovid, Web of Science, MEDLINE-PubMed, and Clinical Key was performed using keywords: sildenafil, tadalafil, PDE5 inhibitors, and muscular dystrophy. Studies were screened for eligibility criteria which included only human studies published in English. Both studies were assessed using the GRADE approach for quality of evidence.
Results: Two studies were included in this systemic review. One was a case-control study to establish functional sympatholysis is impaired in patients with Duchenne MD and with the use of both tadalafil and sildenafil where restoration occurred indistinguishably from healthy controls. The other study performed a case-control initially to establish impaired functional sympatholysis in patients with Becker MD followed by a randomized double-blind placebo controlled crossover trial to test whether tadalafil restored this mechanism. Results were similar in that functional sympatholysis was restored indistinguishably from healthy controls.
Conclusion: PDE5 inhibitors restored functional sympatholysis in all but one patient across both studies. Despite the small sample sizes, very little variability existed across study results leading to receive a moderate level of quality of evidence based on the GRADE approach. These studies were only single-dose trials therefore the need for future studies is needed to assess whether these positive findings will be sustained upon chronic administration. Authors state longer term studies are in progress to assess whether the administration of PDE5 inhibitors can slow disease progression.
Keywords: PDE5 inhibitors, tadalafil, sildenafil, muscular dystrophy
(Click on image to enlarge.)
REVIEWED STUDIES:
Nelson MD, Rader F, Tang X, et al. PDE5 inhibition alleviates functional muscle ischemia in boys with duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology. 2014;82(23):2085-2091. Accessed 20140625.
Martin EA, Barresi R, Byrne BJ, et al. Tadalafil alleviates muscle ischemia in patients with Becker muscular dystrophy. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:162ra155.
AUTHOR: Becky Theisen is currently completing her second year in the School of PA Studies at Pacific University, Oregon. She will graduate with an MS degree in August, 2016.